| [1] |
Yuan LIU, Cheng CUI, Miao YU, Wenyu JIN, Yinliang BAI, Yabin DUAN, Cao FANG, Jianchang HE, Yan HE, Hua HUANG, Shixia HUO, Yang JIN, Lin JIANG, Zhe JIANG, Zheng JIAO, Xuejun LI, Xiangyang LI, Hongjian LI, Lihong LIU, Yang LIU, Hongqiang QIU, Feng SUN, Jianjun SUN, Xuechang WANG, Jianhua WANG, Zhenlei WANG, Shijie WEI, Xiaowen YAN, Lei ZHANG, Xuenong ZHANG, Yuxin ZHANG, Jun ZHAO, Jiye YIN, Ru YAN, Xinchun WANG, Dongyang LIU.
Expert consensus on the value and strategies of precise drug administration for multi-ethnic populations in China
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2026, 31(1): 1-13.
|
| [2] |
WANG Yan, XIA Yuming, ZHU Rendi, OUYANG Ziwei, CHENG Yuanzhi, ZHOU Renpeng, HU Wei.
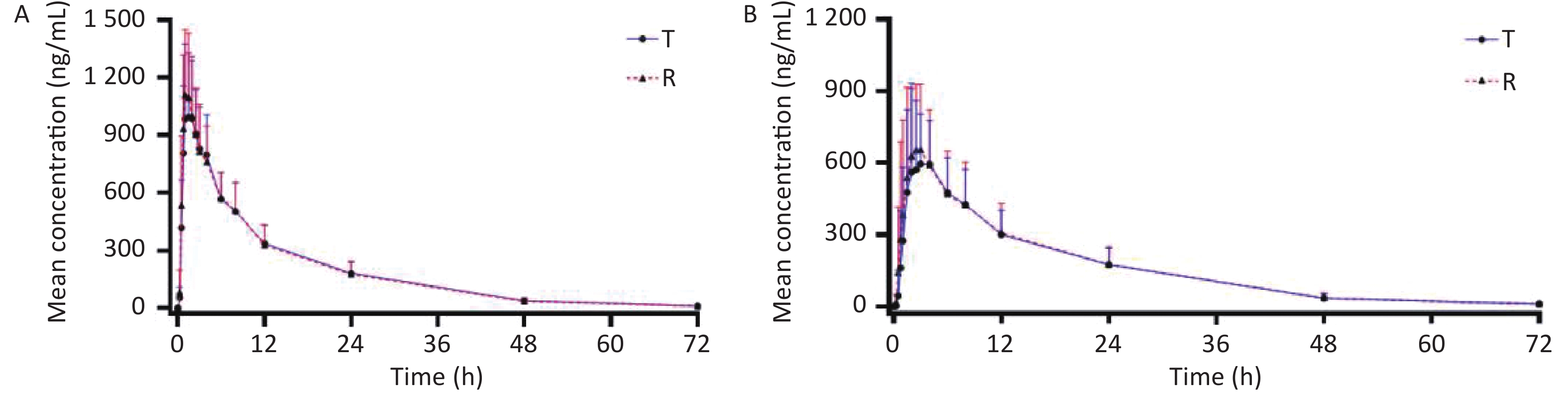
Bioequivalence of ritonavir tablets in healthy Chinese volunteers
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(9): 1193-1199.
|
| [3] |
WEI Yuanyuan1, MA Tao1, TANG Yuezhou1, LI Hubo1, 2, TIAN Xiaoyu1, 2, DANG Yunjie1, ZHOU Xu1.
Individualized dosage study of vitamin D3 based on physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(8): 1067-1075.
|
| [4] |
WU Hao, JIANG Pin, ZHENG Wei, ZHANG Yu, ZUO Jian.
Determination of concentration and pharmacokinetics of protein degradation targeted chimeric drug ARV-471 in mice by LC-MS/MS
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(6): 774-780.
|
| [5] |
HEN Lu, LI Xiaobin, MA Wenxia, XIE Hongyu, WANG Wenping.
Bioequivalence study of rivaroxaban tablets in healthy Chinese subjects
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(6): 789-795.
|
| [6] |
TIAN Yan, YANG Xinyi, LIN Shuangshuang, HE Jinjie, WANG Jingjing, WEI Qiong, HUANG Xingxing, WU Xiaojie.
Study on safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of YZJ-3058 tablets for single oral administration in healthy Chinese subjects
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(6): 796-803.
|
| [7] |
ZONG Jie, HU Xuan, DOU Guifang, MENG Zhiyun, ZHU Xiaoxia, GU RuoLan, WU Zhuona, GUAN Jingli, GAN Hui.
Establishment and application of physiological-based pharmacokinetic model of ertapenem in elderly patients with chronic kidney disease
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(5): 622-630.
|
| [8] |
XIE Jingxian, DU Jianjun, CHEN Lu, ZHANG Lijuan, YANG Yong.
Advances in pharmacokinetics of isavuconazole in special population
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(5): 709-713.
|
| [9] |
MENG Qingheng, HAN Zhihui, LEI Qi, CHEN Bin, YIN Xia, HU Haitang, LIU Hongxia, ZHENG Qingshan, XU Ling, HUANG Qin.
Optimizing the dosing regimen of aripiprazole microspheres by population pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(4): 493-500.
|
| [10] |
DENG Yanru, CAO Gexi, LI Ying, LI Yajing, DONG Zhanjun.
Research progress on pharmacokinetic interactions of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(4): 570-576.
|
| [11] |
ZHANG Qian, YANG Jingjing, WU Juan, ZHANG Qin, QIN Huiling, YU Liang, DU Yijun, HU Wei.
Evaluation of the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic similarity of recombinant human insulin in healthy Chinese volunteers by euglycemic clamp technology
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(3): 385-391.
|
| [12] |
WANG Jianxiong, HU Xiao, MIAO Beibei, ZHANG Lan.
Characteristics and applications in bioequivalence of physiologically based on pharmacokinetic model
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(2): 244-250.
|
| [13] |
LIU Jiahao, ZHANG Erhui, LIU Xiaoping.
Pilot study on pharmacokinetics of HLX43 in rat serum by ELISA
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(12): 1675-1682.
|
| [14] |
GUO Lijia, DONG Zixuan, WU Huizhen.
Research progress of lemborexant in the treatment of insomnia disorder
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(10): 1429-1435.
|
| [15] |
GONG Yan, GONG Weijing, LI Jiaxin, QIN Yanjie, LUO Li.
Population pharmacokinetics of high-dose methotrexate in pediatric patients with diverse malignancies
[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2025, 30(1): 70-77.
|