中国临床药理学与治疗学 ›› 2026, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 14-27.doi: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2026.01.002
新吉乐1( ), 刘晶2, 张欣翼2, 郭家缘3, 韩文卓1, 孙怡馨3, 赵乐1, 冯卫生1, 郑晓珂1,*(
), 刘晶2, 张欣翼2, 郭家缘3, 韩文卓1, 孙怡馨3, 赵乐1, 冯卫生1, 郑晓珂1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-25
修回日期:2025-01-28
出版日期:2026-01-26
发布日期:2026-02-13
通讯作者:
郑晓珂
E-mail:xlz515@163.com;zhengxk.2006@163.com
作者简介:新吉乐,男,博士,讲师,主要从事神经药理学研究。E-mail:基金资助:
Jile XIN1( ), Jing LIU2, Xinyi ZHANG2, Jiayuan GUO3, Wenzhuo HAN1, Yixin SUN3, Le ZHAO1, Weisheng FENG1, Xiaoke ZHENG1,*(
), Jing LIU2, Xinyi ZHANG2, Jiayuan GUO3, Wenzhuo HAN1, Yixin SUN3, Le ZHAO1, Weisheng FENG1, Xiaoke ZHENG1,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-25
Revised:2025-01-28
Online:2026-01-26
Published:2026-02-13
Contact:
Xiaoke ZHENG
E-mail:xlz515@163.com;zhengxk.2006@163.com
摘要:
目的: 筛选调控帕金森病(Parkinson's disease,PD)发病关键基因及相关转录因子表达的小分子化合物。方法: 分析PD患者的基因表达谱数据,筛选PD发病关键基因及转录因子。Connectivity Map(CMap)筛选可调控转录因子表达的小分子药物,并在6-羟基多巴胺(6-OHDA)诱导损伤的PC12细胞和PD小鼠模型评价其PD治疗作用。结果: 维拉帕米(verapamil,Ver)为潜在的候选药物。Ver对6-OHDA损伤的PC12细胞具有保护作用,同时对6-OHDA诱导的PAX5、LEF1、MTF1、IKZF3和SP140等转录因子,以及ITGA6、CDH1、CD40、ESR1、SMAD3、CXCR4等PD发病基因的表达具有调控作用。PD模型小鼠中,Ver可对α-突触核蛋白(α-Syn)表达有一定抑制作用,但对上述PD发病基因及其转录因子和调控作用较弱。结论: Ver对PD的治疗作用部分依赖于对PD发病基因及其相关转录因子的调控作用。
中图分类号:
新吉乐, 刘晶, 张欣翼, 郭家缘, 韩文卓, 孙怡馨, 赵乐, 冯卫生, 郑晓珂. 基于Connectivity Map的药物重定位评价维拉帕米作为治疗帕金森病的药物[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2026, 31(1): 14-27.
Jile XIN, Jing LIU, Xinyi ZHANG, Jiayuan GUO, Wenzhuo HAN, Yixin SUN, Le ZHAO, Weisheng FENG, Xiaoke ZHENG. Connectivity Map-based drug repositioning evaluation of verapamil as a therapeutic agent for Parkinson's disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2026, 31(1): 14-27.

图 1
Fig.1 Differential gene expression analysis A: Box diagram of normalization of samples. The box plot illustrates the transcriptional expression values of the 12 samples in the Parkinson's disease (PD) expression profile dataset GSE169755. B: Differential expression analysis. The volcano plot displays differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with PD onset in the GSE169755 dataset. Red dots indicate downregulated genes, while blue dots represent upregulated genes.

图 2
Fig.2 Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis A: PPI network constructed from PD-onset-associated DEGs. Node color closer to red and larger node size indicate higher criticality. B: GO enrichment analysis results. C: KEGG analysis results.
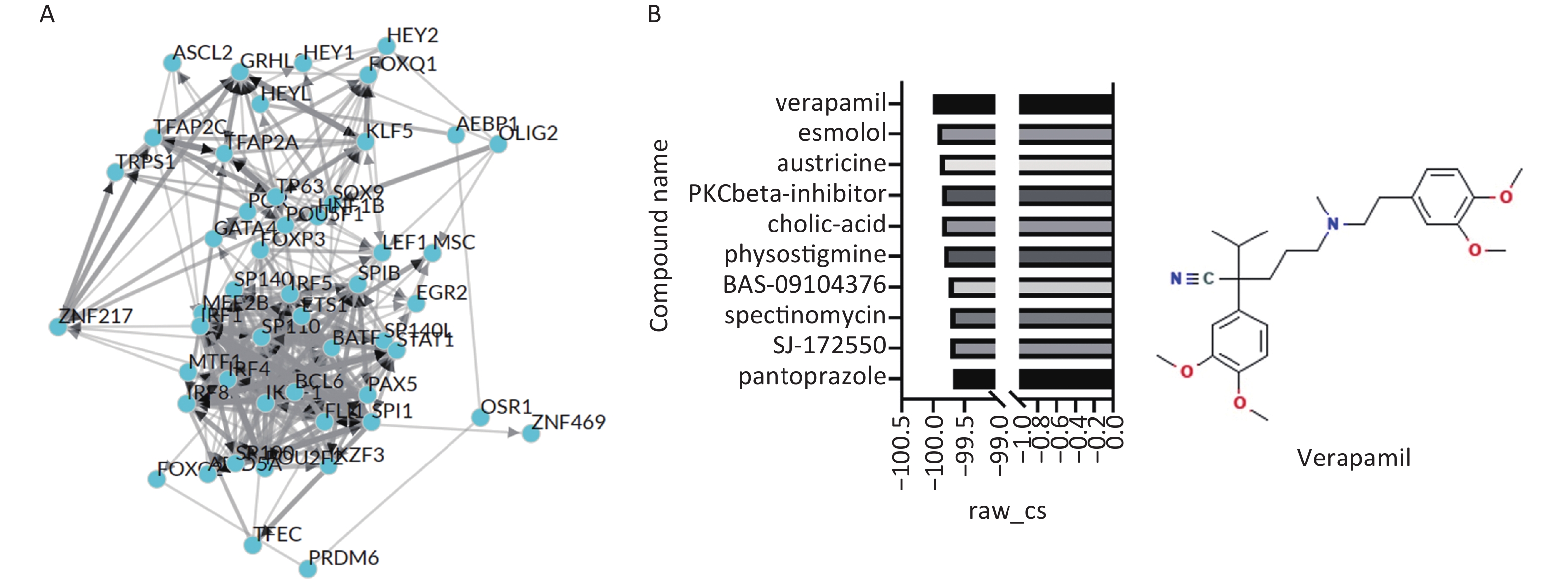
图 4
Fig.4 Transcription factors that regulate hub genes implicated in PD onset and screening of small molecules that regulate the expression of transcription factors A: Regulatory network of transcription factors interacting with PD-associated genes. B: Connectivity Map (CMap) screening for potential small-molecule drugs that modulate the aforementioned transcription factors. The CMap prediction results indicated that verapamil (Ver) exhibited a raw_cs value of -100, the lowest among all compounds, making it the optimal therapeutic candidate.

图 5
Fig.5 Protective effect of verapamil (Ver) against 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells ($ \overline{x} $±s, n=3) A: Cytotoxic effects of 6-OHDA on PC12 cells. B: Effects of Ver on the growth rate of 6-OHDA-induced damaged PC12 cells. C: Effects of Ver on the apoptosis rate of 6-OHDA-induced damaged PC12 cells. bP<0.05, cP<0.01, compared with the control group; fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group.
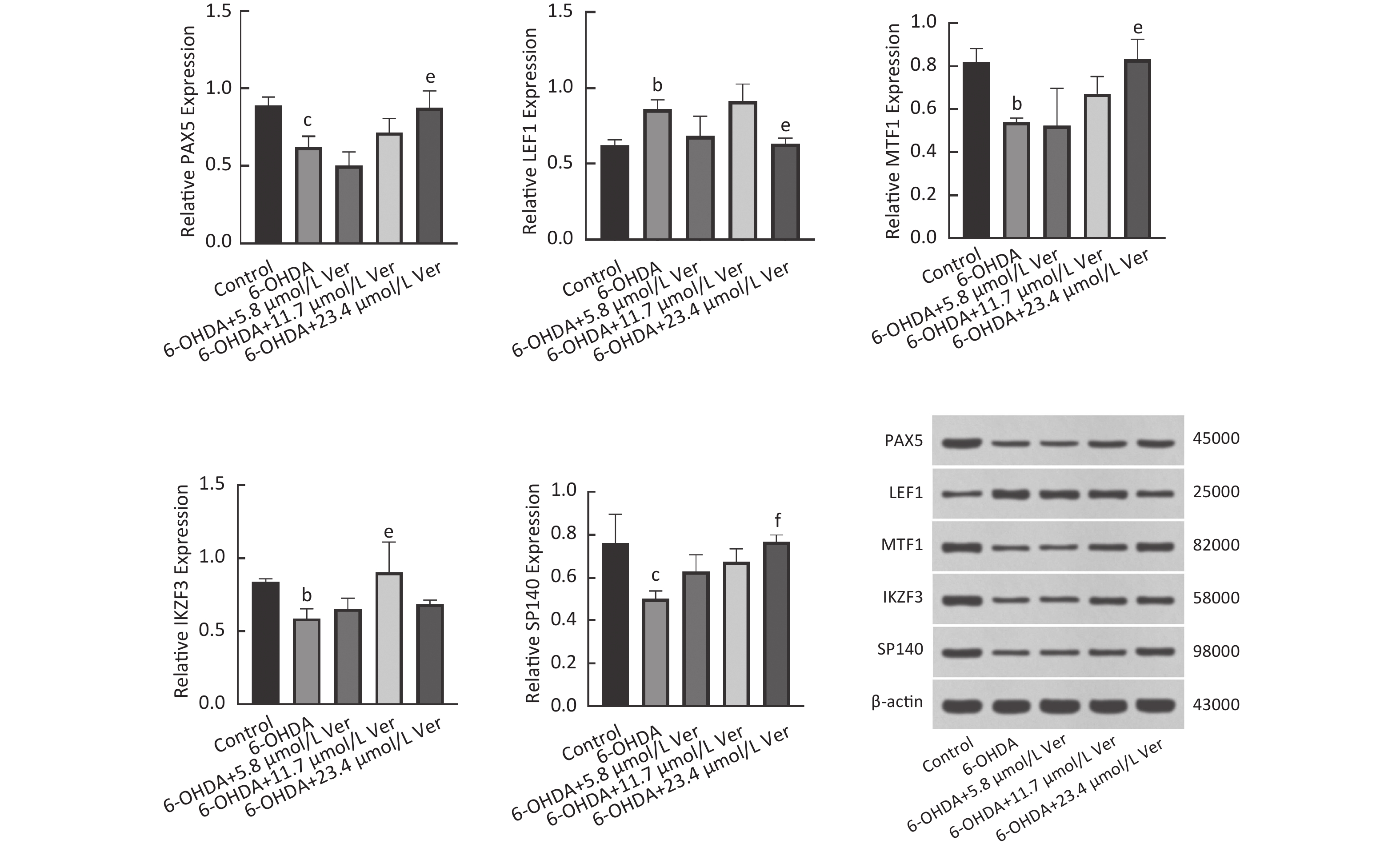
图 6 bP<0.05, cP<0.01, compared with the control group; eP<0.05, fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group.
Fig.6 The regulatory effects of Ver on the expression of transcription factors such as PAX5, LEF1, MTF1, IKZF3, and SP140 in 6-OHDA exposed PC12 cells ($ \overline{x} $±s, n=3) bP<0.05, cP<0.01, compared with the control group; eP<0.05, fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group.

图 7 cP<0.01, compared with the control group; fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group.
Fig.7 The regulatory effects of Ver on the expression of hub genes implicated in PD onset, such as ITGA6, CDH1, CD40, ESR1, SMAD3, and CXCR4 in 6-OHDA exposed PC12 cells ($ \overline{x} $±s, n=3) cP<0.01, compared with the control group; fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group.

图 8
Fig.8 Effect of Ver on tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) expression in a 6-OHDA-induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease ($ \overline{x} $±s, n=6) cP<0.01, compared with the control group; fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group. Scale bar=100 μm; the white arrow represent the TH-positive neuronal cell with brown color.

图 9
Fig.9 Effect of Ver on α-synuclein expression in a 6-OHDA induced rat model of PD ($ \overline{x} $±s, n=6) cP<0.01, compared with the control group; fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group. MFI: mean fluorescence intensity; Scale bar=50 μm; the white arrow represent the α-Syn-positive neuronal cell with red fluorescence.

图 10
Fig.10 Western blot detection of the effect of Ver on the expression of TH and α-Syn in the substantia nigra compacta of the 6-OHDA-induced PD mouse model ($ \overline{x} $±s, n=6) cP<0.01, compared with the control group; fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group.

图 11
Fig.11 The regulatory effects of Ver on the expression of transcription factors such as PAX5, LEF1, MTF1, IKZF3, and SP140 in a 6-OHDA induced rat model of PD ($ \overline{x} $±s, n=6) cP<0.01, compared with the control group; fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group.

图 12 bP<0.05, cP<0.01, compared with the control group; fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group.
Fig.12 The regulatory effects of Ver on the expression of hub genes implicated in PD onset, such as ITGA6, CDH1, CD40, ESR1, SMAD3, and CXCR4 in the 6-OHDA induced rat model of PD ($ \overline{x} $±s, n=6) bP<0.05, cP<0.01, compared with the control group; fP<0.01, compared with the 6-OHDA group.
| 1 |
Isik S, Yeman Kiyak B, Akbayir R, et al. Microglia mediated neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease[J]. Cells, 2023, 12 (7): 1012.
doi: 10.3390/cells12071012 |
| 2 |
Wang S, Jiang S, Wu J, et al. Trends in Parkinson's disease mortality in China from 2004 to 2021: a joinpoint analysis[J]. BMC Public Health, 2024, 24 (1): 1091.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18532-8 |
| 3 |
Calabresi P, Mechelli A, Natale G, et al. Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies: from overt neurodegeneration back to early synaptic dysfunction[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14 (3): 176.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05672-9 |
| 4 |
Muleiro Alvarez M, Cano-Herrera G, Osorio Martínez MF, et al. A comprehensive approach to Parkinson's disease: addressing its molecular, clinical, and therapeutic aspects[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (13): 7183.
doi: 10.3390/ijms25137183 |
| 5 | 祁羚, 李亚楠, 汪瑶, 等. 电针对帕金森病模型小鼠运动功能的影响及相关分子机制探讨[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2024, 47 (5): 721- 728. |
| 6 |
Murakami H, Shiraishi T, Umehara T, et al. Recent advances in drug therapy for Parkinson's disease[J]. Intern Med, 2023, 62 (1): 33- 42.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8940-21 |
| 7 |
Bologna M, Guerra A, Colella D, et al. Objective assessment of the effects of opicapone in Parkinson's disease through kinematic analysis[J]. Neurol Sci, 2024, 45 (5): 2035- 2046.
doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-07233-6 |
| 8 |
Irmady K, Hale CR, Qadri R, et al. Blood transcriptomic signatures associated with molecular changes in the brain and clinical outcomes in Parkinson's disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 3956.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39652-6 |
| 9 |
Cappelletti C, Henriksen SP, Geut H, et al. Transcriptomic profiling of Parkinson's disease brains reveals disease stage specific gene expression changes[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2023, 146 (2): 227- 244.
doi: 10.1007/s00401-023-02597-7 |
| 10 |
van den Hurk M, Lau S, Marchetto MC, et al. Druggable transcriptomic pathways revealed in Parkinson's patient-derived midbrain neurons[J]. NPJ Parkinsons Dis, 2022, 8 (1): 134.
doi: 10.1038/s41531-022-00400-0 |
| 11 |
聂嘉璇, 钱文秀, 王曼姝, 等. 中药毒性相关数据库的研究现状及对比研[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54 (22): 7588- 7596.
doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2023.22.035 |
| 12 |
Lim N, Pavlidis P. Evaluation of connectivity map shows limited reproducibility in drug repositioning[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11 (1): 17624.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97005-z |
| 13 |
Gao L, Zhao G, Fang JS, et al. Discovery of the neuroprotective effects of alvespimycin by computational prioritization of potential anti-Parkinson agents[J]. FEBS J, 2014, 281 (4): 1110- 1122.
doi: 10.1111/febs.12672 |
| 14 |
Fan LY, Yang J, Liu RY, et al. Integrating single-nucleus sequence profiling to reveal the transcriptional dynamics of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21 (1): 649.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04516-6 |
| 15 |
Fletcher EJR, Jamieson AD, Williams G, et al. Targeted repositioning identifies drugs that increase fibroblast growth factor 20 production and protect against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced nigral cell loss in rats[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9 (1): 8336.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44803-1 |
| 16 |
Vargas DM, De Bastiani MA, Parsons RB, et al. Parkinson's disease master regulators on substantia nigra and frontal cortex and their use for drug repositioning[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2021, 58 (4): 1517- 1534.
doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02203-x |
| 17 |
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks[J]. Genome Res, 2003, 13 (11): 2498- 2504.
doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303 |
| 18 |
Keenan AB, Torre D, Lachmann A, et al. ChEA3: transcription factor enrichment analysis by orthogonal omics integration[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47 (W1): W212- W224.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz446 |
| 19 |
Lamb J, Crawford ED, Peck D, et al. The Connectivity Map: using gene-expression signatures to connect small molecules, genes, and disease[J]. Science, 2006, 313 (5795): 1929- 1935.
doi: 10.1126/science.1132939 |
| 20 |
Kalia LV, Lang AE. Parkinson's disease[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386 (9996): 896- 912.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61393-3 |
| 21 |
Blazejewski SM, Bennison SA, Ha NT, et al. Rpsa signaling regulates cortical neuronal morphogenesis via its ligand, PEDF, and plasma membrane interaction partner, Itga6[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2022, 32 (4): 770- 795.
doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhab242 |
| 22 |
Ma S, Li X, Cao R, et al. Developmentally regulated expression of integrin alpha-6 distinguishes neural crest derivatives in the skin[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2023, 11, 1140554.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1140554 |
| 23 |
Li Z, Zhang B, Yao W, et al. APC-Cdh1 regulates neuronal apoptosis through modulating glycolysis and pentose-phosphate pathway after oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2019, 39 (1): 123- 135.
doi: 10.1007/s10571-018-0638-x |
| 24 |
Valdez-Sinon AN, Lai A, Shi L, et al. Cdh1-APC regulates protein synthesis and stress granules in neurons through an FMRP-dependent mechanism[J]. iScience, 2020, 23 (5): 101132.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101132 |
| 25 |
Carriba P, Davies AM. CD40 is a major regulator of dendrite growth from developing excitatory and inhibitory neurons[J]. Elife, 2017, 6, e30442.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.30442 |
| 26 | Ots HD, Tracz JA, Vinokuroff KE, et al. CD40-CD40L in neurological disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23 (8): 4115. |
| 27 |
Cheong RY, Czieselsky K, Porteous R, et al. Expression of ESR1 in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons is essential for normal puberty onset, estrogen feedback, and fertility in female mice[J]. J Neurosci, 2015, 35 (43): 14533- 14543.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1776-15.2015 |
| 28 |
Chen G, Lai S, Jiang S, et al. Cellular and circuit architecture of the lateral septum for reward processing[J]. Neuron, 2024, 112 (16): 2783- 2798.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.06.004 |
| 29 |
Zyuz'kov GN, Miroshnichenko LA, Polyakova TY, et al. The role of Smad3 in the realization of the growth potential of different types of neural progenitor cells and the secretory function of neuroglia[J]. Bull Exp Biol Med, 2024, 177 (1): 35- 38.
doi: 10.1007/s10517-024-06126-8 |
| 30 |
Hiew LF, Poon CH, You HZ, et al. TGF-β/Smad signalling in neurogenesis: Implications for neuropsychiatric diseases[J]. Cells, 2021, 10 (6): 1382.
doi: 10.3390/cells10061382 |
| 31 | Shan Y, Farmer SM, Wray S. Drebrin regulates cytoskeleton dynamics in migrating neurons through interaction with CXCR4 [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021, 118(3): e2009493118. |
| 32 |
Terheyden-Keighley D, Hilla AM, Fischer D. CXCR4 signaling in central nervous system regeneration: friend or foe ?[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2022, 17 (7): 1481- 1483.
doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.330605 |
| 33 |
Maurya SK, Mishra R. Co-localization and interaction of Pax5 with Iba1 in brain of mice[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2018, 38 (4): 919- 927.
doi: 10.1007/s10571-017-0566-1 |
| 34 |
Ohtsuka N, Badurek S, Busslinger M, et al. GABAergic neurons regulate lateral ventricular development via transcription factor Pax5[J]. Genesis, 2013, 51 (4): 234- 245.
doi: 10.1002/dvg.22370 |
| 35 |
Santos R, Linker SB, Stern S, et al. Deficient LEF1 expression is associated with lithium resistance and hyperexcitability in neurons derived from bipolar disorder patients[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2021, 26 (6): 2440- 2456.
doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-00981-3 |
| 36 |
Nouri P, Götz S, Rauser B, et al. Dose-dependent and subset-specific regulation of midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation by LEF1-Mediated WNT1/b-Catenin signaling[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8, 587778.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.587778 |
| 37 |
Valsecchi V, Laudati G, Cuomo O, et al. The hypoxia sensitive metal transcription factor MTF-1 activates NCX1 brain promoter and participates in remote postconditioning neuroprotection in stroke[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12 (5): 423.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03705-9 |
| 38 |
Ferlazzo GM, Gambetta AM, Amato S, et al. Genome-wide screening in pluripotent cells identifies Mtf1 as a suppressor of mutant huntingtin toxicity[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14 (1): 3962.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39552-9 |
| 39 |
Meng C, Chen S, He Q, et al. IKZF3 modulates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting neuroinflammation[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 114, 109480.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109480 |
| 40 |
Fraschilla I, Jeffrey KL. The speckled protein (SP) family: Immunity's chromatin readers[J]. Trends Immunol, 2020, 41 (7): 572- 585.
doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.04.007 |
| 41 |
Karaky M, Fedetz M, Potenciano V, et al. SP140 regulates the expression of immune-related genes associated with multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases by NF-κB inhibition[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2018, 27 (23): 4012- 4023.
doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy284 |
| 42 |
Mokhtari M, Khoshbakht S, Akbari ME, et al. BMC3PM: bioinformatics multidrug combination protocol for personalized precision medicine and its application in cancer treatment[J]. BMC Med Genomics, 2023, 16 (1): 328.
doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01745-y |
| 43 |
Li Y, Gao S, Guo Z, et al. Screening of potential drugs for the treatment of diabetic kidney disease using single-cell transcriptome sequencing and connectivity map data[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2024, 725, 150263.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150263 |
| 44 |
Gao Y, Zhang J, Tang T, et al. Hypoxia pathways in Parkinson's disease: from pathogenesis to therapeutic targets[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25 (19): 10484.
doi: 10.3390/ijms251910484 |
| 45 |
Fang W, Lv P, Geng X, et al. Penetration of verapamil across blood brain barrier following cerebral ischemia depending on both paracellular pathway and P-glycoprotein transportation[J]. Neurochem Int, 2013, 62 (1): 23- 30.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.10.012 |
| 46 |
Li Y, Qiu L, Liu X, et al. PINK1 alleviates myocardial hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 484 (1): 118- 124.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.061 |
| 47 |
叶玲, 叶娟, 鲁继光, 等. 共载多西他赛和维拉帕米脂质体逆转肿瘤耐药性的研究[J]. 药学学报, 2020, 55 (5): 1035- 1041.
doi: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2019-0662 |
| 48 |
Yang T, Ferrill L, Gallant L, et al. Verapamil and riluzole cocktail liposomes overcome pharmacoresistance by inhibiting P-glycoprotein in brain endothelial and astrocyte cells: a potent approach to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci, 2018, 120, 30- 39.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.04.026 |
| 49 |
Lal R, Singh A, Watts S, et al. Experimental models of Parkinson's disease: Challenges and opportunities[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2024, 980, 176819.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176819 |
| 50 |
胡毅龙, 赵怡楠, 苗晋鑫, 等. 大小鼠帕金森病行为学评价方法概述及常用动物模型特点分析[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2024, 32 (7): 942- 954.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2024.07.013 |
| [1] | 许琳琳, 张豆, 丁朋涛, 席晓霞, 杨鹏斐, 张潇亚, 李廷保. 基于TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路探讨过敏煎对特应性皮炎小鼠的保护机制[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2025, 30(12): 1648-1657. |
| [2] | 王欢, 张俊秀, 张雅, 戎浩, 王友娣, 汪五三, 马同军. 圣草酚改善自发性高血压大鼠血管重构的机制研究[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2024, 29(9): 1002-1010. |
| [3] | 王金刚, 李 强, 孙会艳, 王洪权. 鼠尾草酸在帕金森病中的神经保护作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2023, 28(9): 1073-1080. |
| [4] | 李士旭, 李林运, 王 新, 李 轲, 卞 华. 银杏叶提取物通过miR-145/FOXO1轴对实验性肾功能衰竭大鼠肾脏损伤的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2023, 28(7): 728-735. |
| [5] | 汪东辉, 蒋素文, 胡爱荣, 朱 波, 何哲耘, 张露侃, 王家岚, 范 莹, 林 恳. 桑葚改善大鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病的氧化应激损伤[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2023, 28(6): 609-616. |
| [6] | 张志英, 靳秀红, 张小宁, 张向峰, 罗青林, 张松林. TBX21和ADCY9多态性在儿童哮喘发生发展中的临床研究[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2023, 28(4): 407-412. |
| [7] | 陈升富, 李晓琳, 王维刚, 杜玮泽, 李茂星. 中药解热作用研究进展[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2022, 27(3): 334-344. |
| [8] | 樊文香, 张锦璐, 徐驰. α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体在中枢神经系统性疾病中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2021, 26(9): 1065-1072. |
| [9] | 陆宸宇, 杨君, 刘怡希, 郑云. 帕金森氏病关联miRNAs的功能和调控[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2020, 25(7): 775-783. |
| [10] | 冯睿,张佳莉,赫明超,李钺,张岩. 中药及其活性成分防治抑郁症的药理靶点与临床应用[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2020, 25(4): 467-474. |
| [11] | 章水晶, 杜仲燕. 基于网络药理学研究丹参治疗帕金森病的作用机制[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2019, 24(6): 601-607. |
| [12] | 阮水良,官俏兵. 热休克转录因子2通过HMGB1-TLR4-NF-κB信号促进克罗恩病炎症反应的作用机制研究[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2019, 24(4): 369-375. |
| [13] | 杨青霞,毛怡清,张燕芳,薄旭芳. 氟西汀对人结膜上皮细胞TLR2/NF-κB信号通路和炎性因子的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2019, 24(11): 1227-1233. |
| [14] | 沈雅婧,李兰娟. B3型柯萨奇病毒感染对胰岛细胞糖尿病相关LncRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2019, 24(10): 1101-1106. |
| [15] | 常永丽,王春雷,原 丽,郭晓姝,韩玲娜. 外侧隔GABAA 受体在帕金森病模型大鼠焦虑样行为中的作用[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2018, 23(7): 734-742. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||